Accounts of social network users can be compromised in a number of ways. When malware infects a user account, that account can be used to spread spam and malware as well as to gather personal information. Current online systems employ authentication mechanism to verify user’s identities and determine their corresponding authorities. Once authenticated, users are …
Malicious software poses a massive threat to individuals worldwide. Malicious software, or malware, can automate attacks in order to acquire sensitive information or interrupt critical infrastructures. In this study, Thomas Holt and his colleagues looked at malicious software from a criminology point of view. By using a routine activities framework, the authors examined the macro-correlates …
Afin de mieux prédire les vulnérabilités du système, les chercheurs en cybersécurité développent des approches nouvelles et holistiques afin d’identifier les risques. Ce processus d’identification inclue la caractérisation des facteurs humains qui contribuent aux risques et à la vulnérabilité en cybersécurité. Zoe King et ses collaborateurs se sont intéressés plus précisément à la malveillance comme …
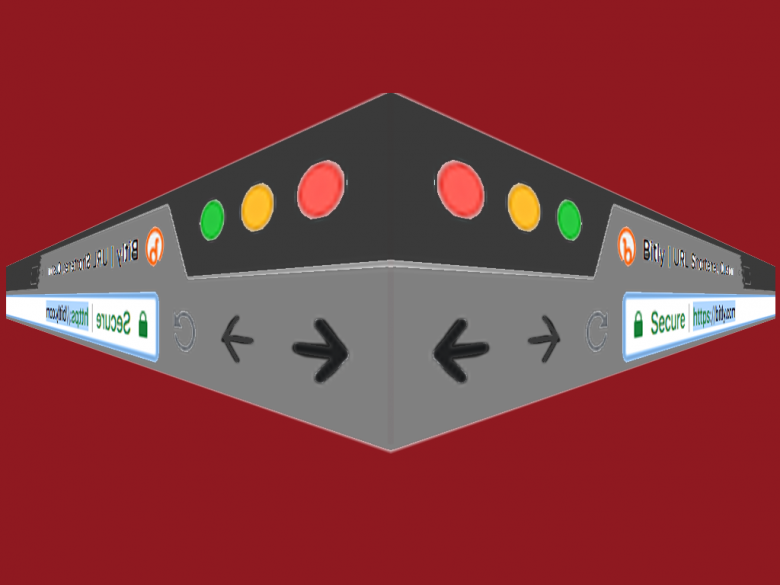
URL shortening services provide a short link in place of a long URL. Attackers sometimes use these services to mask the URL of a malicious destination, making it harder for a person to detect a link that they shouldn’t click on. A group from the university of Ottawa and IBM collected 300 thousand malicious …
The impact of online piracy on companies’ revenues and consumer behavior has been a well-known problem for industry, policy-makers and academics. When it comes to piracy, consumers arguably benefit due to cheaper access to a wider range of content. However, piracy may also inflict significant direct costs, as many piracy sites may be unsafe due …
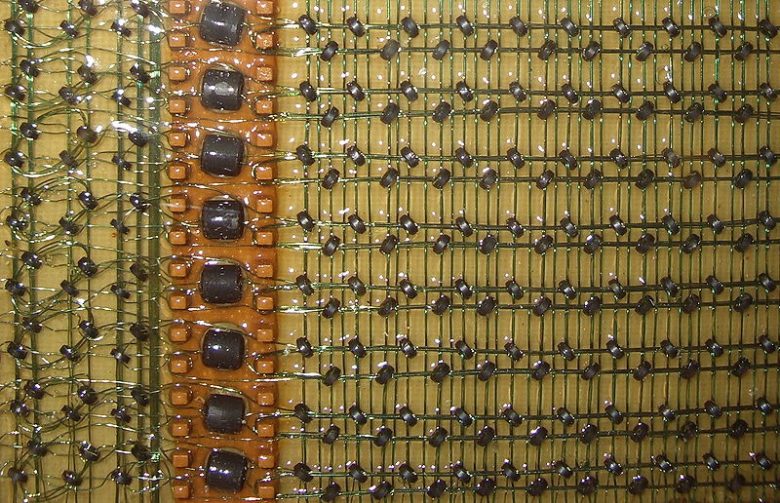
Rowhammer attacks are really interesting. They uses some of the physical properties of how computer memory is designed to overcome the logical control of how it is used. The bits of information are stored so close together in modern memory that if you ‘wiggle’ one bit fast enough, sometimes the ones next to it flip …
Presented by Natalia Stakhanova at the Atlantic Security Conference 2018 Since the first computer virus hit the DARPA network in the early 1970s, the security community interest revolved around ways to expose identities of malware writers. Knowledge of the adversary’s identity promised additional leverage to security experts in their ongoing battle against perpetrators. At the …
At the upper end of security practices there is isolation. Disconnecting a computer from the network and of course the Internet provides a layer of physical control to system access. This air-gap is used to provide a barrier to information theft on individual computers and networks that contain very sensitive data by militaries and organisations. …
Understanding the Simplicity Behind IoT Botnets: A Case Study of a Social Media Fraud Provider Masarah Paquet-Clouston, GoSecure Presented at the SERENE-RISC Workshop, April 2017 Who would want to be liked by an army of robots? The size of a social media account’s audience is considered to be a measure of the influence of a …
A rowhammer attack exploits a vulnerability created by the physical characteristics of modern computer memory. Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM) is a high-speed memory circuit that stores information by creating an electrical charge in tiny capacitor; which is something like a battery. A charged capacitor represents a value (i.e.”1”) as opposed to an uncharged capacitor (“0”). …